CSS position
Jakob Jenkov |
The position CSS property enables you to position HTML elements in different ways than the
normal text flow, and in different ways than the display
CSS property.
The position CSS property can be set to one of these values:
staticrelativefixedabsolute
Each of these values will be covered in the sections below.
position : static
Setting the position to the value static makes the browser render the HTML element
just like normal. In other words, the static value is the default behaviour for HTML elements.
Most often you will not need to set position to static. Instead you would just
not set the position CSS property at all.
position : relative
Setting the position CSS property to relative makes the browser render the HTML
in a position relative to where the HTML element would have been rendered in the normal text and element
flow. To specify where to position the HTML element you have four extra CSS properties:
topleftbottomright
Here is an example that positions an HTML element -20 pixels to the left and -20 pixels above its normal position in the flow:
<style>
#theRelativeSpan {
position : relative;
top : -20px;
left : -20px;
border : 1px solid #cccccc; //shows the boundaries of the element.
}
</style>
<p>
This is a paragraph with a lot of text inside, and a <span id="theRelativeSpan">relative span element</span>
as part of the text.
</p>
This browser screen shot shows how the element is rendered:
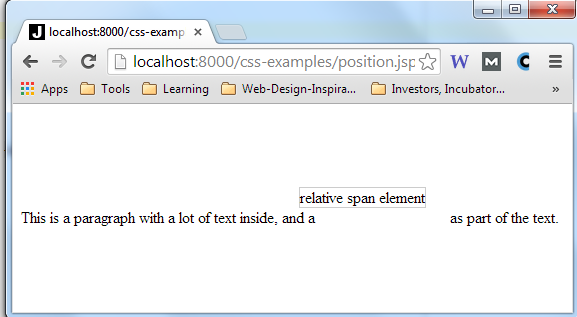
Notice how the span element is rendered to the left and above where it would normally have
been positioned. Notice also, that a blank space is still shown in the place where the span
would normally have been rendered.
position : fixed
Setting the position CSS property to the value fixed makes the HTML element
the property is applied to, be displayed at a fixed position inside the browser window (viewport).
Even if the user scrolls the HTML page vertically or horizontally, or resize the browswer window, the element
remains fixed at the same position inside the browser window.
Here are two browser screen shots which illustrates the effect of the position: fixed CSS property
declaration:
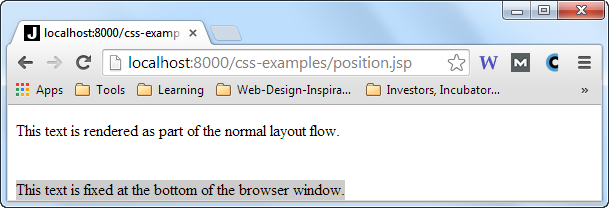
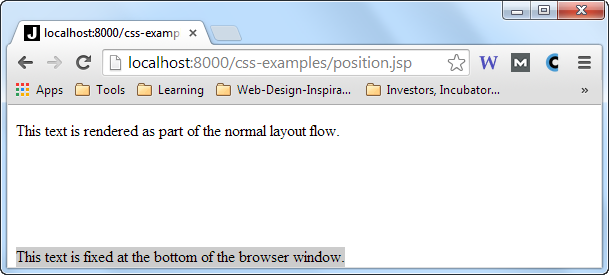
Notice that the browser is a bit taller (the browser was resized) in the second screen shot, but the HTML element with the gray background is still positioned at the bottom of the browser window.
position : absolute
Setting the position CSS property value to absolute works a bit like the fixed
value with some exceptions. Like with fixed the HTML element is positioned relative to the browser
window (viewport), but when the user scrolls horizontally or vertically, the HTML element does not stay at the same
position inside the viewport.
Look at this example code:
<style>
#theAbsoluteDiv {
position: absolute;
bottom : 0px;
background-color: #cccccc;
}
</style>
<div id="theAbsoluteDiv">
This text is positioned with <code>absolute</code> at the bottom of the browser window.
</div>
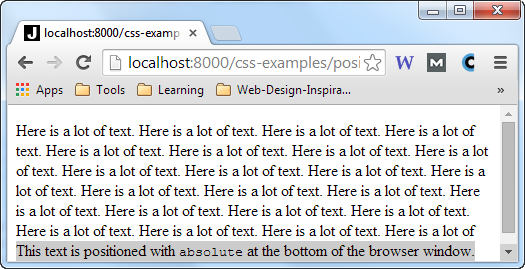
This example sets the div element to position: absolute, positioning the div
element 0 pixels from the bottom of the browser. Here is how that looks when rendered inside a page with more
text:
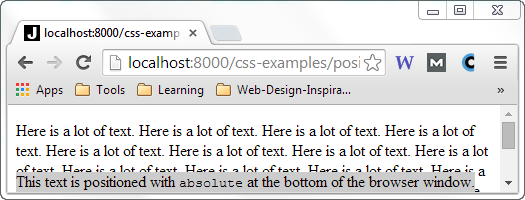
The div element stays relative to the browser window when the browser window is resized.
You can see that in this browser screen shot of the same page, but with the browser resized to be taller:
But, notice what happens when you make the browser window a bit smaller again, and then scrolls a bit down the page.
Now the div element all of a sudden scrolls up on the middle of the screen:
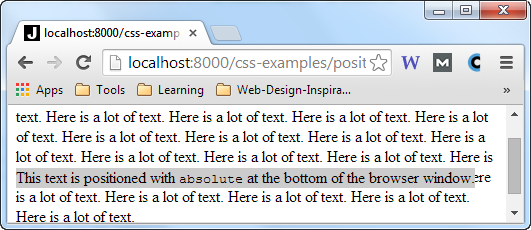
position : absolute Inside Other Positioned Elements
When an element has the position : absolute CSS style applied and that element is nested inside
another element which also has some position value set, then the element with the position : absolute
is positioned absolutely inside the parent element.
Here is an example:
<style>
#theOuterDiv {
position: relative;
top : 0px;
left : 0px;
border : 1px solid #cccccc;
padding : 10px;
}
#theInnerDiv {
position: absolute;
top : 0px;
right : 0px;
padding : 10px;
background-color: #ccffcc;
border : 1px solid #99cc99;
}
</style>
<div id="theOuterDiv">
This is the outer div element.
This is the outer div element.
This is the outer div element.
This is the outer div element.
<div id="theInnerDiv">
This is the inner div element.
</div>
</div>
This example sets position to relative for the outer div element.
Since top and left are set to 0px the outer div element
is positioned exactly where it would have been positioned without setting position to relative.
The inner div element has position set to absolute and top
to 0px and right to 0px. This places the inner div at the
top right corner inside its parent element (because the parent element has position: relative set).
Here is how that looks when rendered in a browser inside a page with more text:
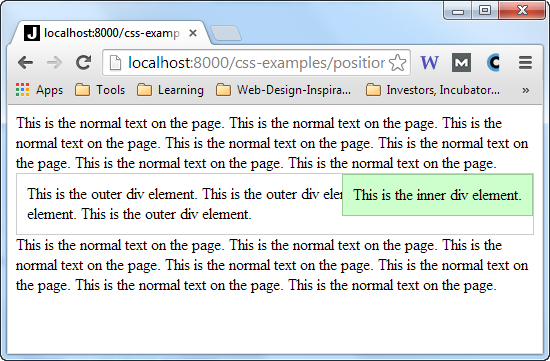
Notice how the position of the inner div is now absolute within its parent element.
| Tweet | |
Jakob Jenkov | |











