JDBC Overview
Jakob Jenkov |
The JDBC API consists of the following core parts:
- JDBC Drivers
- Connections
- Statements
- Result Sets
There are four basic JDBC use cases around which most JDBC work evolves:
- Query the database (read data from it).
- Query the database meta data.
- Update the database.
- Perform transactions.
I will explain both the core component and common use cases in the following sections.
Core JDBC Components
JDBC Drivers
A JDBC driver is a collection of Java classes that enables you to connect to a certain database. For instance, MySQL will have its own JDBC driver. A JDBC driver implements a lot of the JDBC interfaces. When your code uses a given JDBC driver, it actually just uses the standard JDBC interfaces. The concrete JDBC driver used is hidden behind the JDBC interfaces. Thus you can plugin a new JDBC driver without your code noticing it.
Of course, the JDBC drivers may vary a little in the features they support.
Connections
Once a JDBC driver is loaded and initialized, you need to connect to the database. You do so
by obtaining a Connection to the database via the JDBC API and the loaded driver. All communication
with the database happens via a connection. An application can have more than one connection
open to a database at a time. This is actually very common.
Statements
A Statement is what you use to execute queries and updates against the database. There are
a few different types of statements you can use. Each statement corresponds to a single
query or update.
ResultSets
When you perform a query against the database you get back a ResultSet. You can
then traverse this ResultSet to read the result of the query.
Common JDBC Use Cases
Query the database
One of the most common use cases is to read data from a database. Reading data from a database is called querying the database.
Query the database meta data
Another common use case is to query the database meta data. The database meta data contains information about the database itself. For instance, information about the tables defined, the columns in each table, the data types etc.
Update the database
Another very common JDBC use case is to update the database. Updating the database means writing data to it. In other words, adding new records or modifying (updating) existing records.
Perform transactions
Transactions is anoter common use case. A transaction groups multiple updates and possibly queries into a single action. Either all of the actions are executed, or none of them are.
A JDBC Component Interaction Diagram
Here is an example of how the core components interact in during the execution of a database query (click image to view larger version):
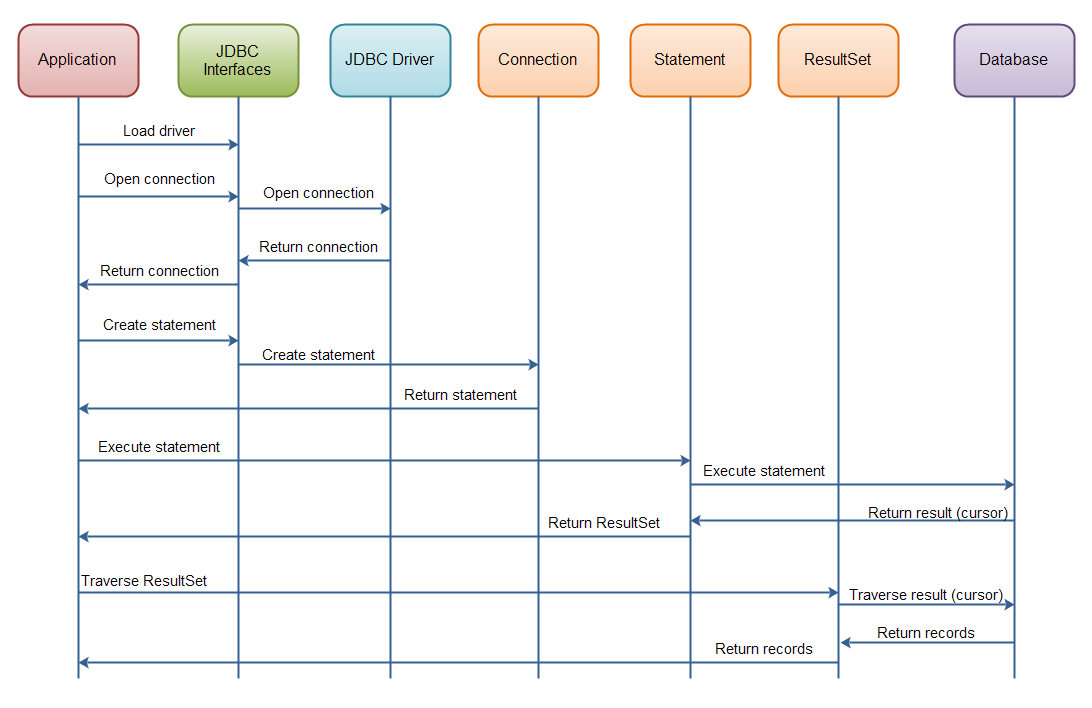 |
| Java JDBC: Interaction of the core JDBC components during the execution of a database query. |
| Tweet | |
Jakob Jenkov | |











