Exchanger
Jakob Jenkov |
Exchanger
The java.util.concurrent.Exchanger class represents a kind of rendezvous point where two
threads can exchange objects. Here is an illustration of this mechanism:
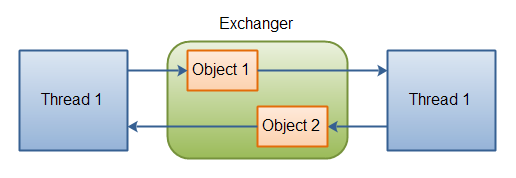 |
| Two threads exchanging objects via an Exchanger. |
Exchanging objects is done via one of the two exchange() methods. Here is an example:
Exchanger exchanger = new Exchanger();
ExchangerRunnable exchangerRunnable1 =
new ExchangerRunnable(exchanger, "A");
ExchangerRunnable exchangerRunnable2 =
new ExchangerRunnable(exchanger, "B");
new Thread(exchangerRunnable1).start();
new Thread(exchangerRunnable2).start();
Here is the ExchangerRunnable code:
public class ExchangerRunnable implements Runnable{
Exchanger exchanger = null;
Object object = null;
public ExchangerRunnable(Exchanger exchanger, Object object) {
this.exchanger = exchanger;
this.object = object;
}
public void run() {
try {
Object previous = this.object;
this.object = this.exchanger.exchange(this.object);
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" exchanged " + previous + " for " + this.object
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
This example prints out this:
Thread-0 exchanged A for B Thread-1 exchanged B for A
Next: Semaphore
| Tweet | |
Jakob Jenkov | |











