JavaFX FlowPane
Jakob Jenkov |
A JavaFX FlowPane is a layout component which lays out its child components either vertically or horizontally,
and which can wrap the components onto the next row or column if there is not enough space in one row.
The JavaFX FlowPane layout component is represented by the class javafx.scene.layout.FlowPane
Creating a FlowPane
You create a JavaFX FlowPane via its constructor. Here is a JavaFX FlowPane
instantiation example:
FlowPane flowpane = new FlowPane();
Adding Children to a FlowPane
You can add children to a FlowPane by obtaining its child collection and add adding the components
to it you want the FlowPane to layout. Here is an example of adding 3 buttons to a FlowPane:
Button button1 = new Button("Button Number 1");
Button button2 = new Button("Button Number 2");
Button button3 = new Button("Button Number 3");
FlowPane flowpane = new FlowPane();
flowpane.getChildren().add(button1);
flowpane.getChildren().add(button2);
flowpane.getChildren().add(button3);
Adding a FlowPane to the Scene Graph
To make a FlowPane visible you must add it to the JavaFX scene graph. To do so you must add
the FlowPane instance to a Scene object, or add the FlowPane to a
layout component which is added to a Scene object.
Here is an example of adding a JavaFX FlowPane to the scene graph:
package com.jenkov.javafx.layouts;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Orientation;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.FlowPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class FlowPaneExperiments extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
primaryStage.setTitle("HBox Experiment 1");
Button button1 = new Button("Button Number 1");
Button button2 = new Button("Button Number 2");
Button button3 = new Button("Button Number 3");
FlowPane flowpane = new FlowPane();
flowpane.getChildren().add(button1);
flowpane.getChildren().add(button2);
flowpane.getChildren().add(button3);
Scene scene = new Scene(flowpane, 200, 100);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application.launch(args);
}
}
The application resulting from this application looks like the following screen shots. Notice how the buttons flow down onto the next horizontal line when the window becomes too small to show them all in a single horizontal row.
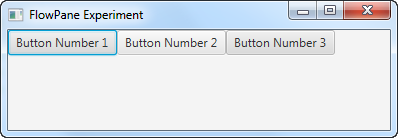
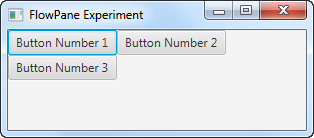
Horizontal and Vertical Spacing
You can set the horizontal and vertical spacing between the components shown inside a JavaFX FlowPane
using its setHGap() and setVGap() methods. Here is an example that shows how to set
the horizontal and vertical gap between components in a FlowPane :
flowpane.setHgap(10); flowpane.setVgap(10);
When added to the example earlier, the resulting application would look like this:
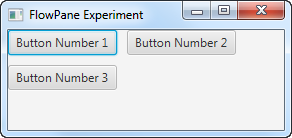
Notice the horizontal and vertical gaps between the buttons now.
Orientation
By default the components in a FlowPane are layed out horizontally, wrapping onto the next horizontal
line when there is no longer space enough inside the FlowPane to show more components horizontally.
You can change the flow orientation (direction) of a FlowPane using its setOrientation()
method. You can force the components to be layed out in columns from top to bottom, and then change column when
there is no more space in the height to show more components. Here is how you do that:
flowpane.setOrientation(Orientation.VERTICAL);
| Tweet | |
Jakob Jenkov | |











