JavaFX Pagination
Jakob Jenkov |
The JavaFX Pagination control enables the user to navigate page by page through content,
for instance pages of search results, articles, images or similar types of content.
The JavaFX Pagination control is represented by the class javafx.scene.control.Pagination.
Here is a screenshot of a JavaFX Pagination control:
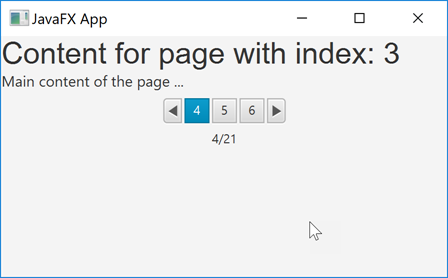
Full Pagination Example
Here is first a full Java code example of how to use a JavaFX Pagination control:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.Pagination;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class PaginationExample extends Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
primaryStage.setTitle("JavaFX App");
Pagination pagination = new Pagination();
pagination.setPageCount(21);
pagination.setCurrentPageIndex(3);
pagination.setMaxPageIndicatorCount(3);
pagination.setPageFactory((pageIndex) -> {
Label label1 = new Label("Content for page with index: " + pageIndex);
label1.setFont(new Font("Arial", 24));
Label label2 = new Label("Main content of the page ...");
return new VBox(label1, label2);
});
VBox vBox = new VBox(pagination);
Scene scene = new Scene(vBox, 960, 600);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
}
Pagination Properties
The JavaFX Pagination control contains a set of properties that specify how the
Pagination control is rendered. These properties are:
- Page count
- Current page index
- Max number of page indicators
The page count is the total number of pages the user can navigate between. The current page index is the page the user is looking at currently. The maximum number of page indicators is the number of shortcut buttons with page numbers on, which the user can click on to navigate directly to that page.
The effect of all three properties are visible in the screenshot earlier in this tutorial. Here is an example of setting all three properties:
Pagination pagination = new Pagination(); pagination.setPageCount(21); pagination.setCurrentPageIndex(3); pagination.setMaxPageIndicatorCount(3);
Pagination Page Factory
The JavaFX Pagination control needs a page factory set on it to be able to navigate properly
through the paged content. The page factory is called when the user navigates to a new page. The page factory
component is attached to the Pagination control via its setPageFactory() method,
and must implement the interface javafx.util.Callback interface.
Here is first how the CallBack interface is defined:
public interface Callback<P,R> {
public R call(P param);
}
In the setPageFactory() method the two type parameters P and R are set to Integer (P)
and Node (R). That means, that the page factory must implement the Callback<Integer, Node>
interface. Here is an example of an implementation of Callback<Integer, Node>:
public static class MyPageFactory implements Callback<Integer, Node> {
@Override
public Node call(Integer pageIndex) {
return new Label("Content for page " + pageIndex);
}
}
The Integer parameter passed to the Callback implementation is the index of the
page the page factory should create a Node for. The returned Node should display
the content for the page with the given page index.
Here is an example of setting the page factory on a JavaFX Pagination control:
pagination.setPageFactory(new MyPageFactory());
You can also set the page factory on a Pagination control using an anonymous Callback
interface implementation, or using a Java lambda expression.
Here is first an example using an anonymous Callback implementation:
pagination.setPageFactory(new Callback<Integer, Node>() {
@Override
public Node call(Integer pageIndex) {
return new Label("Content for page " + pageIndex);
}
});
And here is an example of setting a Pagination page factory using a Java lambda expression:
pagination.setPageFactory((pageIndex) -> {
return new Label("Content for page " + pageIndex);
});
And even shorter, using a shorter lambda expression syntax:
pagination.setPageFactory((pageIndex) -> new Label("Content for page " + pageIndex) );
| Tweet | |
Jakob Jenkov | |











